How Pangea Broke up
There was once a continent that all the Earth's continents were connected to, this continent was called Pangea. Pangea broke up into tiny pieces that formed our continents of today. There were three major phases in the breakage. The first phase was when the supercontinent Lurasia and Gondwana were formed by rifts. Lurasia rotated clockwise towards the North. The next phase is Gondwana split into Africa, South America India and Australia forming a subduction zone and making a trench. The final phase is when Lurasia broke into North America and Greenland. This is how the continents are today and they are still moving.
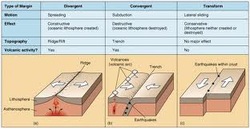
Types of Plate Boundries
A plate boundry is a side of a tectonic plate interacting with another. There are three types of plate boundries. The first one is a divergent boundry which pulls apart and falls down a little , this can cause strato volcanos. Convergent plate boundries are when two plates slide towards each other and one goes under the other. Conservative is when two tectonic plates grind together and form faults. These are the three plate boundries that happen round the edges of the tectonic plates.
Effects on Land
Tectonic plates have an effect on land to, some are good and some are bad. Tectonic plates movement forms hills, mountains, valleys and oceans by plate boundries. Divergent plate boundries form huge mountains and shield volcanoes which form islands like Iceland when the plates move apart to produce gaps which molten lava rises to fill. Divergent plate boundries also form ocean basins and rift valleys like the East African Great Rift Valley. Submarine earthquakes also cause tsunamis.
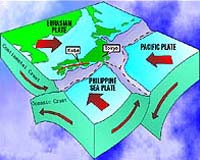
Convergent plate boundries form parallel valleys and large mountain ranges like the Himalayas when the plates collide either buckling, compressing or one plate goes under the other. When two ocean plates collide, islands are formed from volcanoes errupting and deep ocean trenches where the plate dips downwards like Japan. Earthquakes and volcanoes happen because of pressure, friction and plate material melting in the mantle like Mount St Helens.
Conservative boundries or transform boundries are faults which move horizontally. These faults are found on the ocean floor and on land. These form small hills and valleys. The crust in not destroyed or created.
Convergent plate boundries form parallel valleys and large mountain ranges like the Himalayas when the plates collide either buckling, compressing or one plate goes under the other. When two ocean plates collide, islands are formed from volcanoes errupting and deep ocean trenches where the plate dips downwards like Japan. Earthquakes and volcanoes happen because of pressure, friction and plate material melting in the mantle like Mount St Helens.
Conservative boundries or transform boundries are faults which move horizontally. These faults are found on the ocean floor and on land. These form small hills and valleys. The crust in not destroyed or created.